In the realm of weight loss and health optimization, Semaglutide has emerged as a beacon of hope for many struggling with obesity and related health issues. This groundbreaking medication, initially developed for the treatment of diabetes, has shown remarkable efficacy in promoting weight loss, making it a subject of widespread interest and discussion. Through the lens of success stories and the latest research, this blog delves into the transformative journey of individuals who have experienced significant weight loss, shedding light on its potential as a game-changer in the battle against obesity.
Understanding Semaglutide and Its Mechanism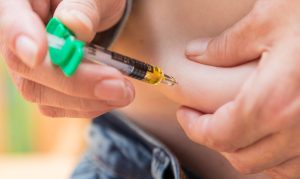
Semaglutide operates by mimicking the action of an appetite-regulating hormone GLP-1, which is naturally produced in the body. By enhancing the body’s own ability to regulate blood sugar and appetite, Semaglutide facilitates a reduction in calorie intake and promotes weight loss. Its effectiveness is not just in numbers on a scale but in its ability to significantly improve cardiovascular health and reduce the risk of obesity-related diseases.
The Journey to Weight Loss: Real-Life Success Stories
The narrative of Semaglutide’s impact is best understood through the stories of those who have walked the path. Individuals from diverse backgrounds, struggling with weight issues for years, have found a new lease on life. These stories often share a common theme: a journey filled with challenges and skepticism, transformed into one of hope, health, and renewal. From significant weight loss achievements to improved health parameters and enhanced quality of life, the success stories of Semaglutide users are both inspiring and affirming.
Weight Loss: Beyond the Scale
The benefits of Semaglutide extend beyond mere weight loss. Users report improvements in blood pressure, cholesterol levels, and blood sugar control, alongside a decrease in the cravings that often derail weight loss efforts. This holistic improvement in health underscores the potential of Semaglutide not just as a weight loss drug but as a catalyst for comprehensive lifestyle change.
Incorporating into a Holistic Health Regimen
For those considering, it’s essential to view it as part of a broader health and wellness strategy. Lifestyle changes, including a balanced diet and regular physical activity, enhance the effectiveness of Semaglutide. Consulting with healthcare professionals to tailor a plan that includes Semaglutide, alongside nutritional and fitness advice, is crucial for achieving the best outcomes.
The Role of DripGym in Supporting Your Wellness Journey
DripGym, a pioneer in wellness and health optimization, offers a range of services that complement the weight loss journey. From IV therapy for hydration and nutrient support to personalized wellness protocols, DripGym provides a holistic approach to health. Their expertise in IV nutrient therapy can play a supportive role in enhancing the body’s overall well-being, making the weight loss journey with Semaglutide even more effective.
Navigating the Path Forward with Semaglutide
As with any medication, the journey with Semaglutide is personal and varies from one individual to another. It’s accompanied by a commitment to lifestyle changes and a proactive approach to health and wellness. The success stories of Semaglutide users not only highlight its potential as a weight loss solution but also illuminate the path for others seeking to overcome obesity and its related health challenges.
The Science Behind Semaglutide
At the core of Semaglutide’s success is its ability to effectively mimic the GLP-1 hormone, which plays a crucial role in regulating appetite and insulin secretion. This mechanism not only aids in controlling hunger but also in improving glycemic control, making it a dual-action solution for weight management and diabetes prevention. The scientific community continues to explore the full potential, with studies indicating its benefits in reducing risk factors for heart disease, stroke, and kidney disease among obese or overweight patients.
Personalized Health Strategies with DripGym
Incorporating Semaglutide into a comprehensive health strategy enhances its effectiveness. DripGym’s innovative approach to wellness, which includes IV nutrient therapy, offers a synergistic effect that can amplify the benefits. By addressing nutritional deficiencies and optimizing hydration, DripGym’s services can help mitigate some of the challenges associated with weight loss, such as fatigue and nutrient imbalance. Their tailored wellness protocols are designed to support the body’s natural healing processes, promoting a state of optimal health that complements the weight loss journey.
The Importance of Community and Support
Embarking on a weight loss journey, especially with the aid of medications like Semaglutide, can be a deeply personal and sometimes challenging experience. The importance of a supportive community and professional guidance cannot be overstated. DripGym not only offers cutting-edge wellness services but also provides a supportive environment where individuals can share their experiences, challenges, and successes. This sense of community is invaluable, offering encouragement and motivation to those on their path to better health.
Looking to the Future
As we look to the future, the success stories of Semaglutide users serve as powerful reminders of the potential for medical innovations to change lives. However, the journey doesn’t stop with medication alone. It’s about embracing a holistic approach to health that includes proper nutrition, physical activity, and mental well-being. DripGym stands at the forefront of this holistic health movement, offering services and support that empower individuals to take control of their health and achieve their weight loss goals.
Final Thoughts
Semaglutide’s role in weight loss and health optimization is a beacon of hope for many. Its success stories are not just about the pounds shed but about the lives transformed. As we continue to explore and understand the full potential of Semaglutide, it’s clear that its impact extends far beyond weight loss. In combination with the holistic health services provided by DripGym, it offers a pathway to a healthier, more fulfilling life. The journey of weight loss is complex and multifaceted, but with the right tools, support, and determination, achieving lasting change is possible.
In conclusion, Semaglutide weight loss is more than a medical breakthrough; it’s a step towards a healthier society. By focusing on the individual’s overall well-being and providing comprehensive support through innovative wellness services like those offered at DripGym, we can look forward to a future where weight management and health optimization are accessible and achievable for everyone.
FAQs
What is Semaglutide?
It is a medication approved by the FDA for weight management in adults with obesity or overweight with at least one weight-related condition (such as high blood pressure, type 2 diabetes, or high cholesterol). It mimics a hormone called glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) that targets areas of the brain that regulate appetite and food intake.
How does Semaglutide work for weight loss?
Semaglutide works by mimicking the action of the GLP-1 hormone, which helps regulate blood sugar, slows down gastric emptying, and reduces appetite. This leads to a decrease in calorie intake and, subsequently, weight loss.
Who is eligible to use Semaglutide for weight loss?
It is prescribed for adults with a body mass index (BMI) of 30 or greater (obese) or 27 or greater (overweight) who have at least one weight-related condition such as hypertension, type 2 diabetes, or dyslipidemia. It’s important to consult with a healthcare provider to determine eligibility based on individual health conditions and medical history.
Are there any side effects of using Semaglutide?
Like all medications, Semaglutide can have side effects. The most common include gastrointestinal issues such as nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, stomach pain, and constipation. Serious side effects can occur but are less common. Always discuss potential side effects with a healthcare provider.
How is Semaglutide administered?
Semaglutide is administered via injection under the skin (subcutaneously). The frequency of the injections depends on the specific formulation of Semaglutide prescribed (e.g., weekly for weight management).
Can Semaglutide be used in combination with other weight loss strategies?
Yes, Semaglutide is most effective when used as part of a comprehensive weight loss strategy that includes diet, exercise, and behavioral changes. Healthcare providers often recommend a holistic approach to weight management.
How does DripGym complement Semaglutide treatment?
DripGym offers IV therapy and other wellness services that can support overall health and complement weight loss efforts with Semaglutide. Services such as hydration drips, vitamin infusions, and nutrient therapy can help manage side effects, boost energy levels, and improve nutritional status, making the weight loss journey more effective and sustainable.
How long does it take to see results with Semaglutide?
Weight loss results with Semaglutide can vary from person to person. Some may see significant weight loss within a few months, while for others, it may take longer. Continuous use under medical supervision, along with lifestyle changes, is crucial for achieving and maintaining weight loss goals.
Is Semaglutide a permanent solution for weight loss?
It can significantly aid in weight loss and improve health markers, but it should be used as part of a long-term strategy that includes lifestyle changes. Weight management is a continuous process, and maintaining a healthy weight requires ongoing effort and support.
Where can I get more information or start treatment with Semaglutide?
For more information or to start treatment, consult with a healthcare provider or a specialist in weight management. They can provide personalized advice and determine if Semaglutide is the right option for you based on your health status and weight loss goals.