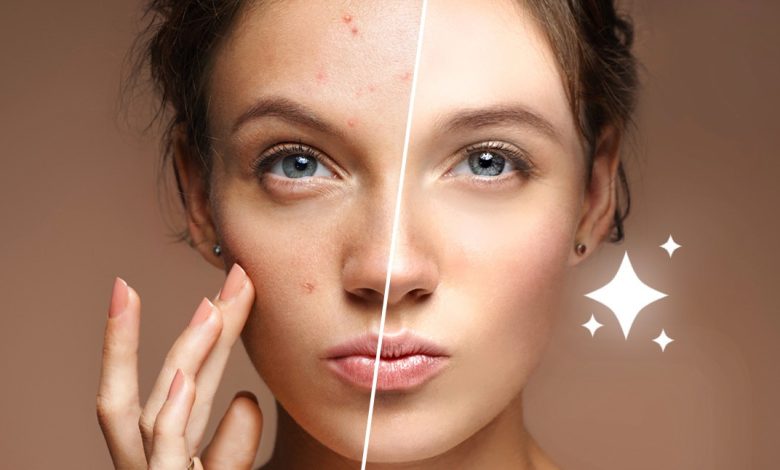
In the ever-evolving world of skincare, ingredients like retinol and retinoid have become buzzwords for those seeking effective solutions to address various skin concerns. In this comprehensive guide, we will unravel the mysteries of retinol and retinoid, exploring their differences, similarities, and the benefits they offer for achieving healthy, radiant skin.
Understanding Retinol and Retinoid:
Retinoids are a class of compounds derived from vitamin A, known for their potent effects on the skin. These compounds play a crucial role in promoting cell turnover, stimulating collagen production, and reducing the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles. However, not all retinoids are created equal, and understanding their distinctions is key to making informed choices for your skincare routine.
- Retinol: Retinol is a type of over-the-counter (OTC) retinoid, commonly found in various skincare products. It is considered a milder form of vitamin A and is converted into the active form (retinoic acid) once applied to the skin. Retinol is known for its anti-aging properties, promoting collagen synthesis and improving skin texture. OTC retinol products are generally well-tolerated and are suitable for individuals who want to incorporate a retinoid into their routine without a prescription.
- Prescription Retinoids: Beyond retinol, there are stronger prescription-strength retinoids, including tretinoin, adapalene, and tazarotene. These prescription retinoids are more potent and directly convert to retinoic acid in the skin. They are commonly prescribed by dermatologists for treating various skin concerns, such as acne, hyperpigmentation, and fine lines. Due to their strength, prescription retinoids may cause more noticeable side effects, including redness and peeling, but they also deliver more dramatic results.
Key Differences:
- Potency: One of the primary differences between retinol and prescription retinoids lies in their potency. Retinol is a milder form that requires conversion to retinoic acid in the skin, while prescription retinoids are already in the active form and exert more immediate and intense effects. The strength of a retinoid is often reflected in its potential side effects.
- Availability: Retinol is widely available in over-the-counter skincare products, making it accessible to a broad range of consumers. On the other hand, prescription retinoids must be prescribed by a dermatologist, and their use should be monitored to ensure proper application and minimize adverse reactions.
- Side Effects: Due to its milder nature, retinol generally causes fewer side effects than prescription retinoids. Side effects of retinol may include mild irritation, redness, or peeling, especially when first incorporating it into a skincare routine. Prescription retinoids can lead to more pronounced side effects, including dryness, flakiness, and increased sensitivity.
- Application Frequency: Retinol is often recommended for daily use, depending on individual skin tolerance. Prescription retinoids, however, may initially be introduced with less frequent application (such as every other night) to allow the skin to acclimate to the potent ingredients. Over time, the frequency may be increased.
Benefits of Retinol and Retinoid:
- Anti-Aging: Both retinol and retinoid are celebrated for their anti-aging properties. They promote collagen production, reduce the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles, and contribute to smoother, more youthful-looking skin.
- Acne Treatment: Prescription retinoids, particularly tretinoin and adapalene, are commonly prescribed for acne treatment. They help prevent clogged pores, promote cell turnover, and reduce inflammation, making them effective in managing acne and preventing breakouts.
- Hyperpigmentation: Retinoids, including prescription variants and retinol, are known to address hyperpigmentation concerns. They can help fade dark spots, sun damage, and uneven skin tone by promoting cell turnover and inhibiting melanin production.
- Improvement of Skin Texture: Both retinol and prescription retinoids contribute to improved skin texture. They work to exfoliate dead skin cells, refine pores, and enhance the overall radiance of the skin.
- Collagen Synthesis: Retinoids stimulate collagen synthesis, a crucial component for maintaining skin elasticity and firmness. This makes them valuable in preventing and treating sagging skin associated with aging.
Incorporating Retinol and Retinoid into Your Skincare Routine:
- Start Slow: Whether you’re using retinol or a prescription retinoid, start with a lower concentration to allow your skin to acclimate. Begin with less frequent applications, such as every other night, and gradually increase as your skin builds tolerance.
- Apply on Dry Skin: Apply retinol and retinoid to dry skin after cleansing. This helps minimize potential irritation, as applying them to damp skin can enhance their penetration.
- Layering with Other Products: Be cautious when layering retinol and retinoid with other active ingredients. Avoid using products with benzoyl peroxide, vitamin C serum, or acids at the same time, as they may increase irritation. Alternatively, use them on alternate nights.
- Use Sunscreen Daily: Sun protection is crucial when using retinol and retinoid, as they can increase skin sensitivity to sunlight.
- Consult with a Dermatologist: If you are considering incorporating retinoids into your routine, especially prescription-strength variants, it’s advisable to consult with a dermatologist. They can provide personalized recommendations based on your skin type, concerns, and goals.
Conclusion:
Retinol and retinoid are powerful ingredients that have revolutionized skincare, offering a range of benefits from anti-aging to acne treatment. Understanding the differences between these two types of vitamin A derivatives is essential for making informed decisions about your skincare routine. Whether you opt for over-the-counter retinol or prescription-strength retinoids, incorporating these ingredients into your regimen can lead to significant improvements in the texture, tone, and overall health of your skin.
It’s important to approach retinol and retinoid with patience, as results may take time to become noticeable. Additionally, being mindful of potential side effects and adjusting your skincare routine accordingly will contribute to a positive experience with these powerful compounds.
Remember, skincare is a journey, and finding the right balance for your unique skin needs may require some experimentation. Embrace the transformative potential of retinol and retinoid, and enjoy the journey toward healthier, more radiant skin. If you have specific concerns or are unsure about which product is right for you, consult with a dermatologist who can guide you on the best approach for your individual skincare goals.